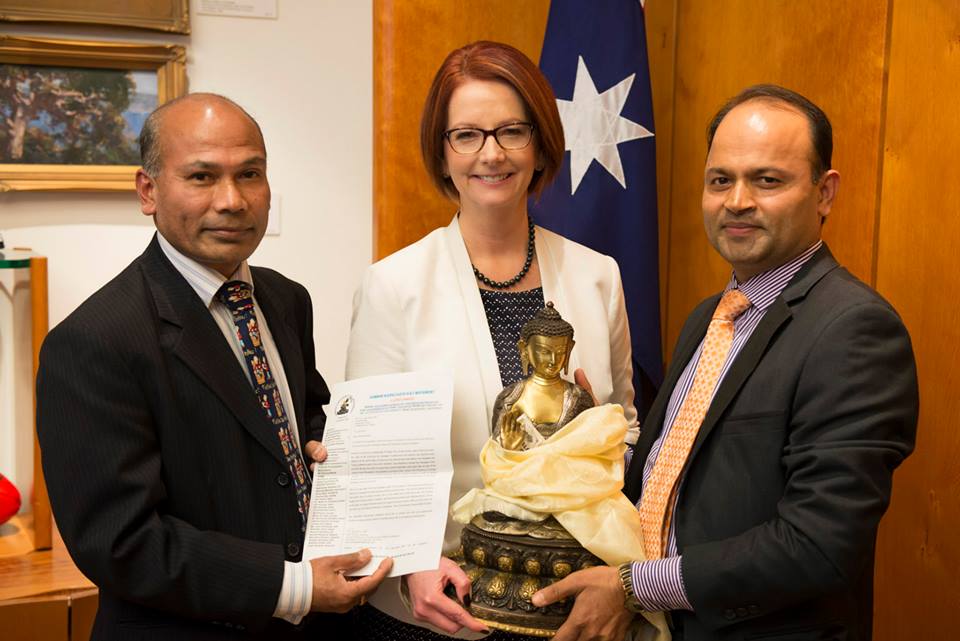
Posted by Ram Kumar Shrestha on November 9, 2011

MOSCOW — Russia launched an unmanned probe on a daring mission to reach Phobos, a moon of Mars, and to fly samples of its soil back to Earth.
The Phobos-Grunt (Phobos-Soil) craft was successfully launched by a Zenit-2 booster rocket at 12:16 a.m. Moscow time Wednesday (2016 GMT Tuesday) from the Russian-leased Baikonur cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
Russia’s Federal Space Agency said the craft separated successfully from the booster about 11 minutes later.
But early Wednesday, the agency said the probe had failed to enter a departure trajectory to shoot off to the Red Planet and remained on a support orbit. The agency’s head, Vladimir Popovkin, told the Tass news agency that the spacecraft’s sustainer engine failed to work.
“There was neither first or second ignition,” he said. “Russia’s space control systems and similar systems of the United States searched the spacecraft on the orbit. It’s fuel tanks have not been thrown off.”
Read the Article at HuffingtonPost
35.387579
-85.962483
Posted in Global, Research | Tagged: Phobos, Phobos Mars Moon, Russia, Russia Mars, Russia Mars Moon, Russia Mission Moon, Russia Moon, Russia Moon Mission, Russia Space Mission, World News | Leave a Comment »
Posted by Ram Kumar Shrestha on August 15, 2011
By Prabha Shrestha
1. BACKGROUND
Cases of HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) are growing rapidly in the world. According to the UNAIDS report in December 1998, 33.4 million people were HIV positive with eleven people infected every minute (JICA brochure).
HIV/AIDS is recognized as an emerging public health problem in Nepal too. NCASC (National Control for AIDS and STD Centre) reported 842 cases of AIDS and 3,600 HIV infections as of November 2004. However, this data could be the tip of the iceberg due to a lack of surveillance data. UNAIDS/WHO estimated approximately 60,018 people in Nepal are living with HIV/AIDS with 2,958 AIDS related deaths in 2002. It is possible that most of the people (60,018) living with HIV/AIDS do not know they are infected and many of them maybe engaging in unsafe sexual practices. It is considered that there is a low disease prevalence in the general population, with a higher prevalence in various sub sets of population such as 68% in IDUs (Intravenous Drug Users) approximately 17% in Sex Workers and 4% in Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) cases (NCASC/MOH, 2003). The consequence of inaction is that AIDS could become the leading cause of death in Nepal over coming years with a serious impact on poverty and vulnerability of the population. Besides the negative impact on socio economic development through loss of productivity, the burden of diseases would put further stress on the health sector.
STI form a significant component of the AIDS/HIV epidemic in Nepal. Unsafe sexual behaviour contributes to a large number of HIV infections. It is estimated that 200,000 cases of STI’s occurs annually and its prevalence in women is about 5%. STI cases among sex workers are considerably high. Syphilis prevalence among Sex Workers (SW) is reported to be 19% in Terai and Kathmandu with a rate of 14% in Pokhara. Similarly, syphilis prevalence is about 5% in the clients of SW (NCASC/MOH, 2004). The provision of early, correct diagnosis and effective STI treatment can not only prevent serious complications but also decrease the chance of HIV spread. However, it is not easy to access services that provide early diagnosis and treatment in a resource poor country such as Nepal.
In order to address the above situation, HMG/Nepal adopted a National Policy for AIDS prevention with 12 key policy statements in 1995. HIV/AIDS and STI prevention program is one of the 12 policy statements. This policy guided NCASC to form the “National AIDS Coordination Committee” and “National AIDS Council” with participation from the government, non-government, private sector and civil society. This helps to operationalise the national policy and advocate for multisectoral participation in the fight against HIV/AIDS. The government is committed to deliver the STI control program with the support of the External Development Partners (EDPs). Read the rest of this entry »
35.387579
-85.962483
Posted in Research | Tagged: AIDS CONTROL AND BLOOD TESTS, AMDA, CARE, DIFID, Eu, EVALUATION OF EQUIPMENT SUPPLY PROGRAM, FHI, FPAN, HIV, IDU, JICA, KfW, MOFA, MOH, Ms Kumiko Yashida, NCASC, Prabha Devi Shrestha, Shinji Yoshiura, STD, SW, TB, TBA, UNAIDS, UNFPA, UNICEF, USAID, WHO | Leave a Comment »
Posted by Ram Kumar Shrestha on August 2, 2011
By Prabha Shrestha
This project outlines a research proposal for the evaluation of a Nepali government program designed and implemented to improve the health status of women in general, and pregnant women in particular. This evaluation proposal has been developed based on Patton’s approach (Patton 1997) because he emphasizes the active participation of the primary stakeholders in the entire process of the evaluation to maximize the utilization of the findings in the program, thus making the program more effective and efficient. Moreover, it suggests that researchers analyze the views of stakeholders in order to determine findings and to form the research committee overseeing the evaluation. As a result, stakeholders may have greater ownership of the findings to make changes in the program since they understand the research process better; it is argued that without the active involvement of the primary stakeholders, the findings may not be utilized in the rural health facilities ofNepal.
the health status of women in general, and pregnant women in particular. This evaluation proposal has been developed based on Patton’s approach (Patton 1997) because he emphasizes the active participation of the primary stakeholders in the entire process of the evaluation to maximize the utilization of the findings in the program, thus making the program more effective and efficient. Moreover, it suggests that researchers analyze the views of stakeholders in order to determine findings and to form the research committee overseeing the evaluation. As a result, stakeholders may have greater ownership of the findings to make changes in the program since they understand the research process better; it is argued that without the active involvement of the primary stakeholders, the findings may not be utilized in the rural health facilities ofNepal.
This evaluation proposal has been designed with the involvement and/or agreement of the commissioner of DoHS to ensure the effective implementation of the evaluation plan and to maximize the utilization of evaluation findings.
1.2 Country context
Nepalhas a multicultural, linguistically, ethnically, and religiously diverse population, derived from the large-scale migrations of Mongoloid groups fromTibet(northern part ofNepal) and Indo-Aryan people from northernIndia(southern part ofNepal) (Asiarecipe, 2003). Indo-Aryan groups consist of the people of Tarai, Pahari, Newar, and Tharus, where as most of the Tibeto-Nepalese groups comprise the Tamang, Kirati (Rai/Limbu), Sherpa and Sunwar. However, it seems difficult to identify who is indigenous and non-indigenous toNepal. Many customs are inherited from both sides and have been developed by the influences of the land, climate and available resources as well. Nepali is the major official language and Hinduism is the major religion (Shrestha 2003) but there are no conflicts among other religions, including Buddhist, Muslim and Christian groups. Read the rest of this entry »
35.387579
-85.962483
Posted in Research | Tagged: Brahmin, Chetri, DHO, DoHS, FCHW, Gurungs, Himalayan region, Kirati, Magars, Masalmans, MCHW, Newars, Prabha Shrestha, Rajbansi, Rajput/Brahman, Satars, Tamang, Thakalis, Tharus | 1 Comment »
Posted by Ram Kumar Shrestha on February 12, 2011
By Dr. Ishara Mahat*
Mountain women in rural Nepal are heavily involved in managing the household energy system. Energy is needed for cooking, heating and processing grain and women often spend about 15 hours per week collecting fuelwood and 15 – 20 hours per week processing the grain needed for family meals. Access to electricity in rural areas of Nepal is just six percent. In 1996, the Rural Energy Development Programme (REDP) was launched to help the government of Nepal achieve its aims of sustainable development and alleviation of rural poverty. The programme aimed to take a holistic and participatory approach to development, including the empowerment of women, and has been recognized as a “best practice” programme in Nepal and internationally. Currently the programme is being implemented in 15 hilly districts in Nepal.
cooking, heating and processing grain and women often spend about 15 hours per week collecting fuelwood and 15 – 20 hours per week processing the grain needed for family meals. Access to electricity in rural areas of Nepal is just six percent. In 1996, the Rural Energy Development Programme (REDP) was launched to help the government of Nepal achieve its aims of sustainable development and alleviation of rural poverty. The programme aimed to take a holistic and participatory approach to development, including the empowerment of women, and has been recognized as a “best practice” programme in Nepal and internationally. Currently the programme is being implemented in 15 hilly districts in Nepal.
Implementation process
The Rural Energy Development Programme primarily focused on micro-hydropower schemes as an entry point to improve the rural energy situation. However, it also promoted solar panels, biogas plants and community development activities such as group savings, literacy programs, construction of roads and wells, dairy collection, poultry farming, mushroom and cardamom cultivation and goat keeping. Activities were implemented through the Village Development Committees, the lowest political and administrative units. The programme facilitated the community mobilization process encouraging women’s participation from the very beginning by forming community organizations of male and female groups. Read the rest of this entry »
35.387579
-85.962483
Posted in Article, Gender, Research | Tagged: Dr. Ishara Mahat, WOMEN IN RURAL NEPAL | Leave a Comment »